Cyprus
 |
|
Contact person for provided information:
Dr Elikkos A. Elia
Department of Lands & Surveys
Senior Lands Officer
29 Michalakopoulou Str., 1455
Nicosia, CYPRUS
eelia (at) dls.moi.gov.cy
Part 1: Country Report
A. Country Context
A.1 Geographical Context
Cyprus is situated in the north-eastern part of the Mediterranean Sea, with an area of 9251 km² and a population of approximately 858,000. Topographically Cyprus consists of two mountain masses (on the north and south) and a central lowland. The Kyrenia Range lies close to the north coast and consists mainly of limestone. To the south is the Mesaoria Plain. The southern half of the island is occupied by the rugged Troodos Mountains, composed mainly of volcanic rocks and reaching a maximum elevation of 1953 m. The agricultural areas have the biggest share with 47.89%, followed by the forest and semi-natural areas, which represent the 44.12% of the total land area of the island. The share of the other categories is much smaller, with the artificial coverage covering 7.63%, followed by wetlands with 0.21% and water with 0.15% of the total area of Cyprus.
A.2 Historical Context
The history of Cyprus goes back 11,000 years.
Cyprus is an island of oceanic origin which has never been connected to the mainland. In the Pleistocen glacial episodes the minimum distance of Cyprus to the mainland would have been 30 km.
- The Stone Age - Neolithic Period I (8th millennium - 4500 BC)
- Neolithic Period II (4500-3500 BC)
- Chalcolithic Period (3500-2500/2300 BC)
- The Bronze Age - Early Bronze Age (2500/2300 - 1900 BC)
- The Middle Bronze Age (1900-1600 BC)
- The Late Bronze Age (1600-1100 BC)
- The Iron Age - Early Iron Age (1100-750 BC)
- The Archaic Period (750-475 BC)
- The Classical Period (475-325 BC)
- The Hellenistic Period (325-30 BC)
- The Roman Period (30 BC-330 AD)
- The Byzantine Period (330-1191 AD)
- Arab Raids (649-965 AD)
- Richard the Lionheart (1191 AD)
- The Frankish Period (1191-1571)
- The Ottoman Period (1571-1878)
- The British Period (1878-1959)
A.3 Current Political and Administrative Structures
Cyprus is an independent, sovereign Republic with a presidential system of government. Under the 1960 Constitution, executive power is vested in the President of the Republic, elected by universal suffrage to a five-year term of office. As of 1 May 2004, Cyprus is a full member state of the European Union.
The executive power is exercised by the President of the Republic. The President exercises executive power through a Council of Ministers appointed by him. Legislative power in the Republic of Cyprus is exercised by the House of Representatives.
On 20 July 1974 Turkey invaded Cyprus. In a two-phase invasion and despite calls by the UN Security Council, Turkey occupied 36.2% of the sovereign territory of the Republic.
A.4 Historical Outline of Cadastral System
The patterns of individual ownership started to emerge, in Cyprus the period after the year 1050 BC. Before that period the system of land tenure was on a purely communal basis.
An inscription of the 5th century BC excavated in Cyprus, and it can be described as a title to land. It mentions that the King of Idalio and the town itself rewarded a physician who had cured those wounded during a siege with the grand of royal lands, of a value of one silver talent, in full ownership. The inscription reveals certain important characteristics of land ownership in ancient Cyprus. It indicates that there were then not only royal lands but also private ownership, mentioned by owner's names. It also indicates the existence of land taxation and of inheritance in those days. The inscription mentions that it was placed under the protection of the priestess of goddess Athena, as a guarantee of title to ownership.
The period 1571-1878, Cyprus is under Turkish Rule. The Ottoman occupation left a deeper mark in the field of land tenure of the island. The most important legal provisions were contained in the Medjelle and the Ottoman Land Code (1857), which set land ownership on a more rational basis. There were five categories of land. The Ottoman System may be described as a system of registration of deeds combined with the registration of title. The parcel boundaries are stated without any reference to a map or plan.
In 1878, an agreement between Great Britain and Turkey transferred administration of Cyprus to Great Britain. In 1907, the Immovable Property Registration and Valuation Law, was enacted. This Law introduced the registration of title and set the basis for the up-to-date registration of all immovable property, based on the plan in use.
In 1946 the Immovable Property (Tenure Registration and Valuation) Law came into operation. It embraces a sound system of registration and it is committed to universal registration.
The principal components of the Cyprus system include the register and the cadastral plans. The system of land registration is that of title. A registered person is considered to be the undisputed owner and his title to ownership is absolute, subject to the Lands and Surveys Department Director's power to correct errors or omissions and to the inherent power of the courts to order an amendment. The authority responsible for the operation of land registration is the government through the Director of DLS. In Cyprus, no transfer of, or change on any immovable property is valid unless registered in the District Lands Office. Title is not guaranteed by the State and there is no indemnity fund; but the whole system is highly trusted by the public.
The registration is based on cadastral plans, which are linked to the national grid and cover the whole island. All lands, including state lands, appear on register. The cadastral plans are prepared and kept up-to-date by the state. The boundary points are not necessarily marked on the ground.
B. Institutional Framework
B.1 Government Organizations
Land registration and cadastral surveying in Cyprus is undertaken, at national level, by the Department of Lands and Surveys (DLS), of the Ministry of Interior. DLS is the oldest department in the government service, dating back to 1858. The initial and main responsibility of the Department was the registration of immovable property on the island. However, throughout the years, the Department expanded its services and activities offered to the public, emerging into a dynamic and multifaceted organization.
B.2 Private Sector Involvement
The private sector is not involved in the official land or cadastral registration. The private sector can only be involved as consultants or advisors to a client in particular cases. Licensed surveyors, since 2.2.2007, can carry out cadastral surveys, which are submitted and approved by DLS. The private surveyors had a limited involvement in cadastral surveys, before the 2.2.2007.
B.3 Professional Organization or Association
The 100 private licensed surveyors in Cyprus are registered by the Cadastral Survey Council, which is the Organization responsible for the private cadastral surveyors and the law for carrying out cadastral surveys. The President of the Cadastral Survey Council is by the law the Director of DLS. Cadastral Surveys in Cyprus used to be carried out by government surveyors working in DLS. Today, approximately 80 government surveyors continue to work in cadastral surveying.
B.4 Licensing
There is a licensing system in place for Cadastral Surveying Professionals. To become a licensed surveyor there is a demand to be a member of the Rural and Surveying Engineers Section of the Cyprus Scientific and Technical Chamber and have at least one year experience in cadastral surveys.
B.5 Education
In Cyprus the Cyprus University of Technology (Department of Civil Engineering and Geomatics) offers a degree for cadastral surveying professionals. Licensed surveyors are also graduated, after following a five-year course, from the National Technical University of Athens or the Technical University of Thessaloniki.
C. Cadastral System
C.1 Purpose of Cadastral System
The cadastral system in Cyprus supports the legal ownership of land, land transfer, land valuation, and the definition, identification, demarcation, measuring and mapping of legal parcel boundaries. Today the cadastral system plays a fundamental role in broader land administration activities. Through the computerization of spatial and textual data the cadastre now serves a multipurpose role supporting many activities. These include supporting land management and planning, land development, local government and utilities management and many other multipurpose functions.
C.2 Types of Cadastral System
The Cyprus cadastral system is one unified system valid for all types of land including governmental land.
C.3 Cadastral Concept
The cadastral system in Cyprus is operated in such a way that land parcels are surveyed in the field while the corresponding land ownership titles are recorded in the Land Registry. The Land Registry uniquely identifies each parcel corresponding to the title. The basic unit of the cadastral system is the "immovable property". Buildings, flats, wells and other immovable properties are also registered and related to land parcels.
C.4 Content of Cadastral System
The cadastral system maintains the Land Register in which the immovable property is recorded. In the Land Registry the ownership of the property is kept as well as other information including the value of the property, restrictions, mortgages and encumbrances. The land registry data has been totally computerized.
D. Cadastral Mapping
D.1 Cadastral Map
Cyprus is wholly covered by cadastral survey, which according to the method used and the degree of accuracy is classified into the following categories:
Unsound Survey: It was carried out between 1904 and 1911, for the preparation of cadastral plans on scale 1:2500. It is in fact a chain survey method, but the available control was very rare. It covers part of Famagusta district.
Chain Survey: The Chain Survey method was used after the establishment of the triangulation in 1915. All field measurements were recorded in field books. Cadastral plans on scales from 1:500 to 1:2500 were prepared and used for the general registration.
Plane table: By 1919 it was realized that, the survey of the island could not be completed by 1929, which was the time target set. Chain survey was a slow method and it was decided to survey the remainder of the island by the method of plane table. The plans at scale 1:5000, produced by this method were used later for the sporadic registration of properties.
Resurvey: The resurvey project started the last few years, in order to replace all existing cadastral plans with new ones, on scales 1:1000 and 1:2000. This project involves the comparison of information from various sources (like existing cadastral plans, field surveyed data and photogrammetric data).
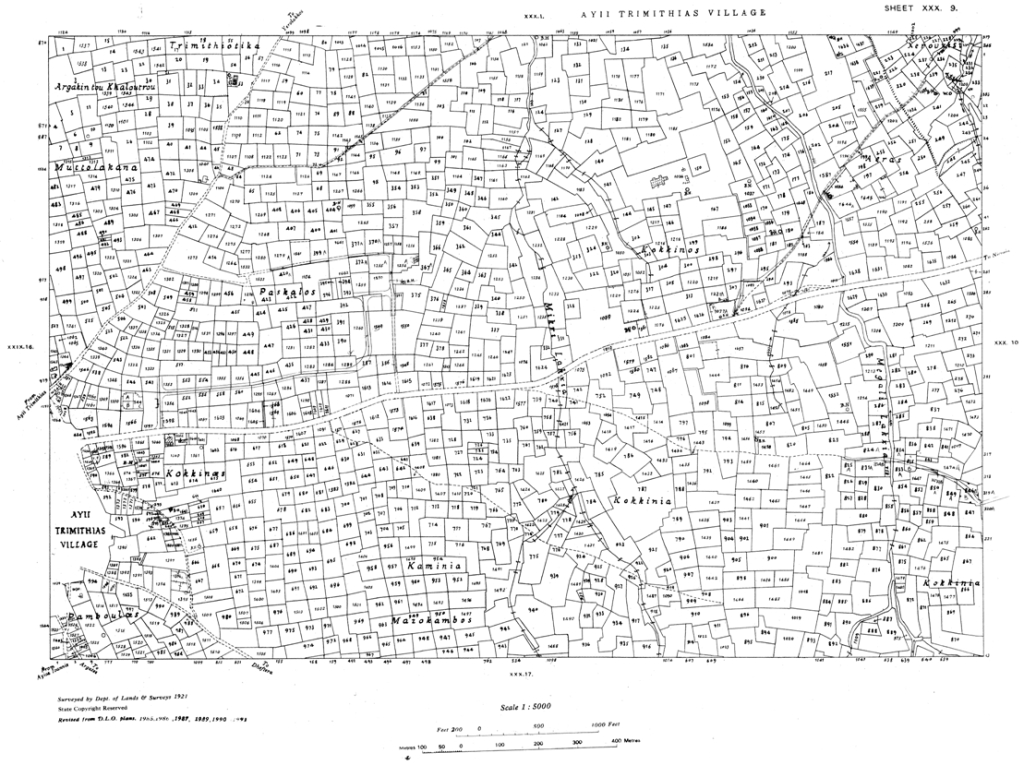
Figure 1: Example from a cadastral map.
D.2 Example of a Cadastral Map
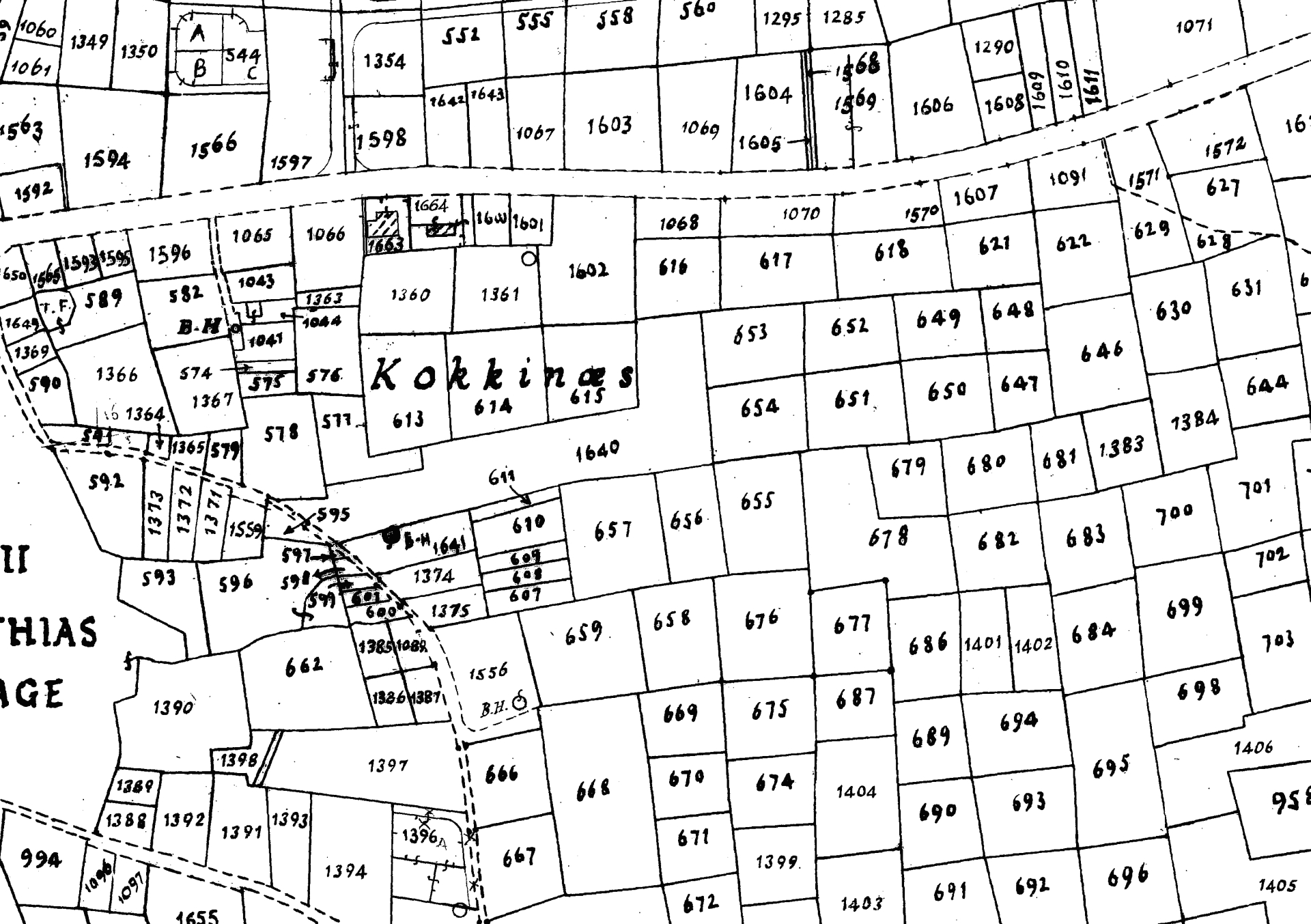
Figure 2: Extract from cadastral map in Fig. 1.
D.3 Role of Cadastral Layer in SDI
Cyprus, through the Lands and Surveys Department, managed to implement a fully integrated Land Information System (LIS), which supports a wide range of decision-making elements, including land conveyancing, the application of equitable taxation, resource management and environmental planning.
The LIS has been designed and developed having two major application components:
- The Survey Related Applications (Geographical Component)
- The Legal/Fiscal Applications (Legal/Fiscal Component)
Four main databases have been developed in the Department:
- The Survey Database,
- The Digital Cadastral Database,
- The Topographical Database, and
- The Legal/Fiscal Database.
The cadastral index map is widely used in land administration as reference and for planning purposes. It is available in digital format, raster or vector (Digital Cadastral Database).
The cadastral map plays a fundamental role and it formulates the basis for the development of a National Land Information System. Other spatial data sets are integrated with the cadastral map layer, including topographic data, administrative boundaries, planning zones.
E. Reform Issues
E.1 Cadastral Issues
Moving from the first inaccurate cadastral map to the new accurate cadastral map.
The resurvey project started in the last few years, in order to replace all existing cadastral plans with new ones, on scales 1:1000 and 1:2000. The process that is followed is very slow because there is a need to compare information from various sources (like existing cadastral plans, field surveyed data, photogrammetric data, and previous applications). In the areas in which the resurvey is completed the Digital Cadastral Data Base is replaced by the Survey Data Base.
Need to improve efficiency, accessibility and service level
There is a need to improve efficiency, accessibility and service level through investigation of customers' needs and through re-engineering (including legislation reforms) and development of internet applications and e-government procedures.
Need for closer cooperation between organizations
There is a need for closer cooperation between various organizations dealing with spatial data to avoid duplication of effort and to ensure uniform and homogeneous coverage of spatial and aspatial data for the whole island.
E.2 Current Initiatives
A new resurvey program has been established to speed-up the project and which take advantage of all sporadic surveys that carried out. The Cyprus Government adopted in December 2005 the European strategy towards implementing electronic governance under the e-Europe2005 project.
After the successful operation of an Integrated Land Information System, which satisfies the needs of the Department of Lands and Surveys, the development of a National Integrated Land Information System can now take place.
The INSPIRE directive aims to create a European Union (EU) spatial data infrastructure. This will enable the sharing of environmental spatial information among public sector organizations and better facilitate public access to spatial information across Europe. In Cyprus, the Ministry of Interior has undertaken the coordination of the implementation of INSPIRE Directive. The Department of Lands and Surveys and the Department of Environment have undertaken a leading role in the organization and the implementation of INSPIRE Directive targets. The Department of Information Technology Services has also undertaken an important role in the technical support part. A new law proposal was prepared in 2009, which was later, on 14.5.2010, approved by the Parliament. The spatial data infrastructure (SDI) in Cyprus is heavily based on the data, produced and maintained by the Department of Lands and Surveys, which are stored within the Land Information System (LIS). The SDI will fulfill most of the requirements of government departments, services, semi-government organizations and the private sector. The new law will harmonize the spatial data that are maintained by several bodies and it will secure the classification and distribution.
F. References
www.moi.gov.cy/dls
www.cyprus.gov.cy
www.mof.gov.cy/cystat
Cyprus Department of Lands and Surveys' Reports
Part 2: Cadastral Principles and Statistics
1. Cadastral Principles
1.1 Type of registration system |
|
title registration
deeds registration |
1.2 Legal requirement for registration of land ownership |
|
compulsory
optional |
1.4 Approach for establishment of cadastral records |
|
systematic
sporadic both, systematic and sporadic all properties already registered |
2. Cadastral Statistics
2.1 Population |
858,000 |
2.2a Population distribution: percentage of population living in urban areas |
69 |
2.2b Population distribution: percentage of population living in rural areas |
31 |
2.3 Number of land parcels |
1,585,000 |
--- Number of land parcels per 1 million population |
1,847,300 |
2.4 Number of registered strata titles/condominium units |
290,000 |
--- Number of strata titles/condominium units per 1 million population |
337,900 |
2.5 Legal status of land parcels in URBAN areas: |
|
percentage of parcels that are properly registered and surveyed |
100 |
percentage of parcels that are legally occupied, but not registered or surveyed |
0 |
percentage of parcels that are informally occupied without legal title |
0 |
2.6 Legal status of land parcels in RURAL areas: |
|
percentage of parcels that are properly registered and surveyed |
90 |
percentage of parcels that are legally occupied, but not registered or surveyed |
10 |
percentage of parcels that are informally occupied without legal title |
0 |
2.7 Number of active professional land surveyors |
180 |
2.8 Proportion of time that active professional land surveyors commit for cadastral matters (%) |
90 |
--- Approx. full-time equivalent of land surveyors committed to cadastral matters |
162 |
2.9 Number of active lawyers/solicitors |
2,400 |
2.10 Proportion of time that active lawyers/solicitors commit for cadastral matters (%) |
10 |
--- Approx. full-time equivalent of active lawyers/solicitors committed to cadastral matters |
240 |