Latvia
 |
|
Contact person for provided information:
Lelde Rozentale
State Land Service
Project Manager
11.novembra krastmala 31, Riga, LV-1050, Latvia
lelde.rozentale@vzd.gov.lv
Part 1: Country Report
A. Country Context
A.1 Geographical Context
Latvia is to be found in the North-eastern Europe, on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea. It is the central country of three Baltic States (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania). The territory of the Republic of Latvia is 64 589 square kilometers. The length of state border is 1368 km, but the length of the coastline – 498 km. Latvia borders Estonia, Russia, Belarus and Lithuania. The capital of the state is Riga, almost one third of the population of the state lives there (at the beginning of 2013 – 696 618).
The landscape of Latvia is marked by lowland planes and hills. The average altitude of Latvia is 87m over sea level. Inland-waters cover 2,543 km2 or approximately 4% of the territory of country. In Latvia, there are totally 777 rivers that are longer than 10 km, and approximately 2256 lakes that are greater than 1 ha. Forests cover 45% of territory, agricultural land – 39.3%.
Population of Latvia approximately is 1.987 574 million (Nov. 2015), Latvians make 61.4%, Russians – 26.0%, Belarusians – 3.4%, and other nationalities – 9.2%.
A.2 Historical Context
Latvian ancestors Proto-Balts arrived in the territory of nowadays Latvia in the first half of the 2000 BC. In the 900s AD the ancient Balts began to establish specific tribal realms and gradually four Baltic tribal cultures developed: Couronians, Latgallians, Selonians, Semigallians. Starting from 1200s, when German Crusaders invaded the territory of Latvia, until the beginning of 1900 the territory of Latvia was under rule of other countries. In thirteenth century a confederation of feudal nations Livonia was developed under German rule. After the Livonian War (1558 – 1583) Latvian territory came under Polish-Lithuanian rule, later after the Polish-Swedish war (1600 – 1629), part of the territory passed under Swedish rule. It can be considered that consolidation of the individual tribes into Latvian nation occurred in the 1600s.
At the beginning of the 1700s, during the Great Northern War Russia conquered the part of territory of Latvia that had been under Swedish rule and by the end of the 18th century the whole territory of Latvia was under Russian rule. The latter half of the 1800s marked a period of national rebirth, and the situation shaped after the First World War made it possible to establish the independent state of Latvia on November 18, 1918. In the 1930s, likewise as in many other European countries, an authoritarian regime was established in Latvia. The existence of an independent state was interrupted in 1940 by Soviet occupation. From 1941 until 1944 it was replaced by German occupation. In 1945, Soviet occupation was reinstated and it remained until 1990-1991, when taking advantage of liberalization of communist regime, pro-independence forces managed to achieve restoration of the independence of Latvia. Since 2004, Latvia is member country of European Union and NATO.
A.3 Current Political and Administrative Structures
Latvia is democratic, parliamentary republic with unitary structure of state. The country's head of state is the President, who is elected by the parliament for a period of 4 years. The President performs mainly representative functions. Legislative power is in the hands of a single chamber parliament – the Saeima that is elected in general, equal, direct, secret and proportional elections for a period of 4 years. Executive power is performed by Cabinet of Ministers consisting of ministries and headed by Prime Minister.
In Latvia there are 119 municipalities – 110 districts and 9 cities.
A.4 Historical Outline of Cadastral System
As in many other countries, cadastre historically was established in Latvia for the classification and registration of properties in order to tax them according to their quality and quantity. As territory of Latvia was under the rule of other countries from 1200s until the beginning of 1900s, development within cadastral sector was defined by policies and interests realized by these countries.
Beginnings of land accounting in Latvia can be found already in Middle Ages. In 900s – 1200s classification of land possessed by farmers in cadastral measurement units – ‘aratrum’ – was started in the territory of Latvia in order to define impost and corvee. In 1500s-1600s land surveying and valuation was started. Under Swedish rule from 1683-1693 the first cadastre that was based on unified land surveying and valuation methodology was established in the territory of Latvia. Methodology and data of Swedish cadastre were used for more than 200 years.
Changes in land administration occurred when serfdom was abolished - since 1860 farmers started to buy out their land, thus tasks of cadastre included preparation of information for purposes of calculation of land buy-out price, arrangement of and preparation of ownership documentation for property registration. Vidzeme’s cadastre (1861-1912), as well as later Latvian state cadastre (1931-1940) performed real estate valuation instead of land valuation.
After the establishment of Latvian state in 1918, one of the most important tasks was the land reform that was performed in 1920–1937. Initially, cadastral data of Vidzeme compiled before the First World War were used, but they covered only approximately one third of territory of the country. Cadastral Law of the independent Latvia was adopted in 1931. It prescribed to carry out cadastral surveying of the territory of the country, producing of plans and cadastral valuation of real estate. Latvia developed its own real estate cadastre and system for its maintenance. Also Land Book that performed registration of ownership was established.
When Soviet rule established in 1940 and land nationalization was performed, state cadastre system of Latvia ended its existence. However, during the period of occupation due to activities of leaders of land utilization systems, significant work was done in taking of aerial photographs of territory, soil mapping, land account and valuation.
History of contemporary cadastre of Latvia started in 1992, simultaneously with land reform that was necessary, when independence of state of Latvia was regained and transition to market economics took place. Land ownership for natural persons officially was restituted 1993. New institution was established – State Land Service. The first eight years of operation of National Real Estate Cadastre Information System (Cadastre Information System) were devoted mainly to data collection and initial registration, but since 1997 Cadastre Information System had to cover all the real estates and its components – land parcels and buildings to serve for Real Estate Tax administration. Regular Mass assessment of all land parcels and buildings is carried out to prepare actual mass values for each real estate. From year 2001 data updates and quality is the main priority. 100% of the territory of country is registered in Cadastre Information System that is organized in digital form. On December 1, 2005 new Law on National Real Estate Cadastre was adopted by parliament of Latvia.
Another institution – Land Registry that was restored in 1993, registers ownership.
B. Institutional Framework
B.1 Government Organizations
1. The State Land Service
The State Land Service (the “SLS”) is a governmental institution of the Republic of Latvia. SLS is in charge of real property object data accumulation and dissemination to institutions responsible for land management and supervision. The SLS is supervised by Minister of Justice.
The main tasks of the SLS are as follows:
- provision of the State Information System of real property cadastre and registration of real property object data – registration and updating of textual and spatial data on land units, buildings, groups of premises, parcels of land, system maintenance and development of Real Property market data base maintenance, provision of data accessibility in on-line mode;
- maintenance of textual and graphical information in the State Address Register – textual and spatial addressing objects registration and updating, system maintenance and developing, drafting and updating of administrative territory border descriptions and graphical data;
- mass valuation of real property - land units, buildings, groups of premises, parcels of land, the development of cadastral value base, determination of special values;
- implementation of national land reform policy – maintenance of Rural Land Privatization Register, taking decisions on renewal of land proprietary rights or transfer of land into ownership for payment in rural areas, consideration of border disputes in rural area, organization of state funded land cadastral surveying for former proprietors;
- provision of the operation of high detailed elaboration topographic data central database – accumulation of high resolution topographic data of all state territory;
- maintenance of Information System of encumbered territories – registration and updating the data encumbered territories and object;
- cadastral surveying of buildings and groups of premises – obtaining textual and spatial data of buildings and groups of premises for updating the information in the State Information System of Real Property Cadaster, management of cadastral and land survey methodology.
The SLS consists of head office and five Regional Offices. Regional Offices comprises thirteen offices, which provide customer service in twenty eight customer service centers.
Until 2006 SLS performed also surveying and mapping functions. In the result of reorganization of SLS that took place at the end of 2005 since January 1, 2006 surveying function (except cadastral surveying of buildings) is delegated to private sector and to newly established State Limited Company “Latvia State Surveyor”. Functions of geodesy, mapping and of producing basic data of state geographic information and building and maintaining its infrastructure are performed by newly established government agency “Latvian Geospatial Information Agency”.
2. Land Registry
Real property ownership registration is carried out by Land Registry under Land Register Department of Court Administration and 28 Land Register offices of regional courts. According to Law on Land Register, all 28 Land Book databases are merged in State Unified Computerized Land Register (SUCLR), so SUCLR is central database, where it is possible to get information on all properties registered in Land Register in Latvia.
The Land Books provides registration of:
Real property as mortgage unit (incl. land together with buildings, buildings without land, apartments and non-residential premises);
- property rights (who is owner and which is legal background);
- restrictions on property rights (easements, encumbrances, usage limitations etc.);
- easement (servitude) as rights on usage another property;
- mortgages;
- other rights connected to the property (lease holders, will agreements etc.).
B.2 Private Sector Involvement
Private sector is involved in performance of several functions related to:
- engineering surveying (setting out construction objects, high detail topography, establish of geodetic networks);
- land planning;
- cadastral land surveying.
Engineering surveying, land planning and cadastral land surveying in Latvian carried out only by certified persons.
In cooperation with the State Land Service, surveyors receive data via data publication portal www.kadastrs.lv. After preparation and electronic submission of cadastral surveying files in the State Land Service, the data from cadastral surveying files are assessed and registered in Cadastre Information System.
B.3 Professional Organization or Association
Latvian Association of Surveyors
Surveyors and specialists working in surveying sector are joined in Latvian Society of Surveyors (LSS). It is professional non-governmental organization that aims at promotion of technical and scientific development of surveying and at protection of surveyors’ professional and social interests.
Latvian Association of Cartographers and Geodesists
Association of Cartographers and Geodesists is a public organization. Its main aim is to promote development and to raise prestige of the cartography and geodesy fields.
B.4 Licensing
In Latvia there are license (certificate) required for every surveyor. It is regulated by regulation “Order for person certification and certified person supervision in geodesy, land planning and land cadastral surveying”. Surveyor can get three kinds of certificate:
·engineering surveying (setting out construction objects, high detail topography, establish of geodetic networks);
·land planning;
·cadastral land surveying.
There are two authorities in Latvia who issue and supervise certification: Certification center of Latvian Association of surveyors (sc.lmb.lv) and Education center ABC (www.abc.edu.lv).
Requirements to get certificate for land cadastral surveying are: at least bachelor degree or second level higher education in geodesy or program related to geodesy (e.g. cartography, spatial planning), and at least two year experience working as surveyor within last 5 year period (described by work contract or table of executed works). Examination is carried out in form of test, containing 30 questions. Time limit is 60 minutes and to pass examination there must be 25 correct answers. Certificate is valid for 5 years.
The total number of licensed land surveyors in Latvia is 308.
B.5 Education
In Latvia, two universities offer education in cadastral surveying and land surveying programs.
Latvia University of Agricultural offers 5-year professional bachelor program in land surveying with engineering bachelor degree in land surveying. Post-graduate 2-year program is available with MSc. ing. degree.
Riga Technical University offers 4.5-year bachelor professional program in geomantic with engineer qualification in geodesy and cartography. Post-graduate 2-year academic program is available receiving MSc. ing. in civil engineering (geodesy). Riga Technical University since 2005 offers new 4-year bachelor professional program in real property management receiving real property economist qualification and bachelor degree in real property management. Post-graduate program for master degree will be available.
C. Cadastral System
C.1 Purpose of Cadastral System
To provide society with up-to-date information on real property, which consists of data on land units, buildings, groups of premises, parcels of land, owners, holders and users.
Cadastral data are used for:
- corroboration of real property rights;
- formation of transactions with real property;
- use and planning of real property development
- cadastral valuation;
- real property tax administration;
- economic development and territorial planning at state, regional and municipal levels;
- land and environmental planning;
- preparation of statistical information;
- preparation of land balance;
- development and maintenance of geographic information system;
- securing interests of different register and information system holders;
- other purposes.
Thus cadastre has multi-purpose role.
C.2 Types of Cadastral System
There is one unified real property National Real Estate Cadastre Information System (the–Cadastre Information System), covering the total territory in Latvia. The system covers the total territory regardless of ownership and land use.
There is no information available on illegal settlements in Cadastre Information System.
C.3 Cadastral Concept
In Cadastre of Latvia, basic uniquely identified and surveyed unit is a land parcel that is defined as a delimited piece of land registered in the Cadastre Information System having cadastral designation assigned to it. Likewise buildings, groups of premises and parts of land parcels (defined for rental purposes) are also surveyed, identified and registered in Cadastre Information System. Also real properties that are defined as land with buildings and waters lying thereon that are juridical attached to natural or juridical person are registered in cadastre. Rights to real properties are registered in Land Register.
In Latvia, there are four types of real property:
- real property consisting of land;
- real property consisting of land and buildings;
- real property consisting of buildings;
- residential property.
Dividing land as a property type, real property should be understood in a wider sense, ie. land, buildings and constructions, belonging to the land owner which may also include a vacant land parcel. Building property is real property which consists only of buildings, located on the land of another owner. Residential property in an apartment building, where flats belongs to individual owners, each owner has a separate real property together with joint property undivided share.
C.4 Content of Cadastral System
Latvia belongs to those countries which have 2 separate registers, maintained by two institutions: The State Land Service and Land Registry.
Real property registration and formation is carried out by the State Land Service and real property ownership registration is carried out by Land Register.
Cadastre Information System is a unified system, which provides approved up-to data textual and spatial data, of the Republic of Latvia on land units, buildings, groups of premises, parcels of land as well as owners, legal possessors, users, real property tax objects and real property tax payers.
Content of Cadastre Information System has gradually increased: if during the first four years from its reinstating only land parcels and land properties and land assigned for use were registered, in the beginning of 90th years also registration of building data was started and since 2000 – mass registration of residential properties. Also procedures of valuation of land, building and residential properties are carried out in Cadastre Information System, as well as registration of archive files is carried out.
Cadastre consists of:
- textual data - location of real property, cadastral designation and area of land parcels, buildings and constructions, groups of premises, value of real property and encumbrances and restrictions on real property, as well as on the owner, legal possessor or the user.
- spatial data – cartographic images with the borders of land parcels and buildings, cadastral designations and other information on real property.
Both, textual and spatial data in Cadastre Information System are organized only in digital (vector) form, and connection is ensured between textual and spatial part.
Data for Cadastre Information System are registered using:
- land cadastral surveying documents;
- building cadastral surveying documents;
- documents issued by local governments and state institutions;
- other state information systems: State Unified Computerised Land Register, Population Register, Register of Enterprises , State Register of Forests, State Address Register etc.
In Cadastre Information System there are registered approximately 96 % of buildings and 100 % of land parcels.
D. Cadastral Mapping
D.1 Cadastral Map
Cadastral map is digital (in form of vectors) in Latvia. It covers the whole territory of the Republic of Latvia and serves for overview on location of depicted objects in the territory. Map is created in Latvian coordinate system LKS-92 in TM projection; it is obtained by method of alignment of boundaries of parcels. Cadastral maps are stored in the Central Database.
The cadastral map includes the following elements:
- boundaries, names, codes and numbers of cadastral territories and cadastral groups;
- boundaries, frontier posts and cadastral designation of land units;
- outline and cadastral designation of buildings;
- identificator and border of the territory with encumbrance on the use of real property;
- boundaries, frontier posts and cadastral designation of parts of land parcels.
Technical specification of cadastral map has published on the State Land Service website www.vzd.gov.lv
D.2 Example of a Cadastral Map
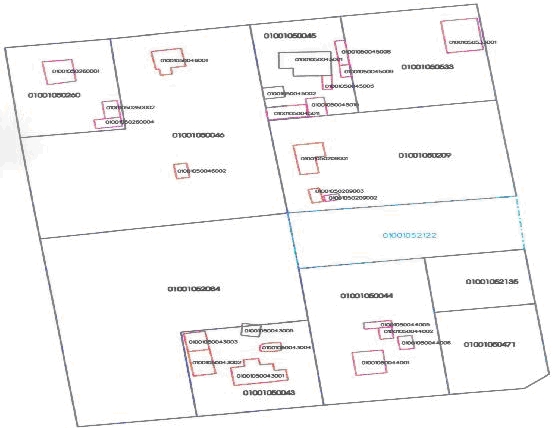
Figure 1: A fragment of a cadastral map.
D.3 Role of Cadastral Layer in SDI
Cadastral map is consistent part of Latvian map system; it is one of thematic maps. Information of Cadastral map can be used for following purposes:
- ascertainment of location of specific cadastral object (objects);
- overview on location of cadastral objects in certain area;
- territory planning;
- changing of boundaries of administrative territories;
- other purposes, where Cadastral map obtained by method of alignment of boundaries can be used.
Cadastral map is compatible with following cartographic material:
- simplified topographical map at scale of 1:10,000;
- topographic plan at scale of 1:2,000;
- topographic plan at scale of 1:500 for separate areas;
- graphical part of State Address Register;
- map of boundaries of administrative territories;
- other thematic maps.
SLS data distribution portal www.kadastrs.lv is developed to ensure that every person can have an on-line access to textual and spatial data of Cadastre Information System and State Address Register. The portal has Public and Authorized access areas. Data in publicly-accessible area of the distribution portal is free of charge. When customer wants to receive detailed information from the portal, it will be a paid service.
E-Portal www.latvija.lv gives the opportunity for every owner, legal possessor or user to access information on real property 24/7 free of charge through the e-service “Mani dati Kadastrā”, state institutions and local governments can access online information using graphical and textual web service, replication of data base, FTP server or portal kadastrs.lv
E. Reform Issues
E.1 Cadastral Issues
1. The geographical data under responsibility of the SLS are entered, maintained and processed in non-integrated and separate systems or in graphical files, using different software and technology platforms.
2. Latvia belongs to those countries which have 2 separate registers, maintained by two institutions: The SLS and Land Registry. Real property registration and formation is carried out by the SLS while real property ownership registration is carried out by Land Register. There exists data inconsistency between both Information Systems; the data are incomplete and incompatible.
3. Quality and actuality of data in Information Systems maintained by the SLS.
4. Obsolete data of buildings in Cadastre Information System.
E.2 Current Initiatives
1. In 2015 the project “The State Land Service Geospatial Data Geographical Information System Development” was finalized. As a result geospatial modulus of encumbered territories, value zoning, cadastral surveying of buildings and multifunctional geospatial portal for the clients were implemented.
2. To ensure complete data quality and harmonization of Information Systems, “Conception of National Real Estate Information System and State Unified Computerized Land Register Data Base Development as Unified Information System” has been aprooved providing synchronized National Real Estate Information System and State Unified Computerized Land Register data base. For implementation of the Concepcion a new development project “Modernization of Cadastre Information System and Development of Data Services” started on 2015.
3.For simplification of procedures and integration of services between Cadastre and Land Register before implementation of the Conception 8 services of integrated procedures in aforementioned information systems developed on 2015.
4. In 2012 “Conception of Improvement of Cadastral Valuation System and assurance of Cadastral Data Up-to-dateness” was approved by the Cabinet of Ministers. The aim of the conception is to ensure high quality cadastral valuation data which is highly consistent with real estate market values and are more comprehensible to the general public. Regulations and laws necessary for implementation of valuation related functions of the Concepcion has been approved.
5. Conception of Process Development of Buildings Cadastral Surveying provides that starting from 2014, Building Information System (BIS) will serve as a source for detailed data of buildings. Data exchange with Building Information partially started on 2015.
6. Development of new Law on State Cadastre started on 2015.
F. References
www.vzd.gov.lv
Part 2: Cadastral Principles and Statistics
1. Cadastral Principles
1.1 Type of registration system |
|
title registration
deeds registration |
1.2 Legal requirement for registration of land ownership |
|
compulsory
optional |
1.4 Approach for establishment of cadastral records |
|
systematic
sporadic both, systematic and sporadic all properties already registered |
2. Cadastral Statistics
2.1 Population |
1,986,100 |
2.2a Population distribution: percentage of population living in urban areas |
68 |
2.2b Population distribution: percentage of population living in rural areas |
32 |
2.3 Number of land parcels |
1,814,800 |
--- Number of land parcels per 1 million population |
913,700 |
2.4 Number of registered strata titles/condominium units |
596,813 |
--- Number of strata titles/condominium units per 1 million population |
300,400 |
2.5 Legal status of land parcels in URBAN areas: |
|
percentage of parcels that are properly registered and surveyed |
82 |
percentage of parcels that are legally occupied, but not registered or surveyed |
16 |
percentage of parcels that are informally occupied without legal title |
2 |
2.6 Legal status of land parcels in RURAL areas: |
|
percentage of parcels that are properly registered and surveyed |
81 |
percentage of parcels that are legally occupied, but not registered or surveyed |
16 |
percentage of parcels that are informally occupied without legal title |
3 |
2.7 Number of active professional land surveyors |
308 |
2.8 Proportion of time that active professional land surveyors commit for cadastral matters (%) |
70 |
--- Approx. full-time equivalent of land surveyors committed to cadastral matters |
215 |
2.9 Number of active lawyers/solicitors |
125 |
2.10 Proportion of time that active lawyers/solicitors commit for cadastral matters (%) |
10 |
--- Approx. full-time equivalent of active lawyers/solicitors committed to cadastral matters |
12 |