Macao
 |
|
Contact person for provided information:
Mr. Cheong Sio Kei
Cartography and Cadastre Bureau
Acting Director of Cartography and Cadastre Bureau
Estrada de D. Maria II, no.32-36, Edificio CEM, 5th floor, Macao Special Administrative Region, China
dscc (at) macau.ctm.net
Part 1: Country Report
A. Country Context
A.1 Geographical Context
The Macao Special Administrative Region (MSAR), being part of the China Territory, is located at the Pearl River Delta of the southeastern coast of Mainland China. The territory, 26.8 sq km in area, consists of the Macao Peninsula, Taipa Island and Coloane Island - the Macao Peninsula is connected to the Taipa Island by two bridges and the two islands are connected by reclaimed lands. The highest peak, of 170.6 m in height, is located on the Coloane Island. Macao has undergone many substantial changes in shape and size over its history. In the last century alone Macao has more than doubled its land area.
The population is approximately 441.6 thousands, with about 95 percent of the population Chinese and 5 percent Portuguese, Europeans and from other countries. More than 85 percent of the population resides in the Macao peninsula, others in Taipa and Coloane Island, as well as the maritime area.
A.2 Historical Context
Macao was a former Portuguese Colony from the 16th century to 1999. In 1985 Lisbon announced the opening of negotiations with Beijing on the transfer of sovereignty to the People's Republic of China. The final settlement, which was signed in 1987, provided for a handover in 1999 after which Macao would become a 'Special Administrative Region' within China. The Basic Law of the Macao Special Administrative Region was adopted by the National People's Congress (NPC) on March 31, 1993, as the constitutional law for Macao taking effect on December 20, 1999.
A.3 Current Political and Administrative Structures
The Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China is headed by the Chief Executive. The Administration, the executive arm of the Government, is organised into the Government Secretariat and departments. Departments implement laws and policies and provide direct services to the community.
The MSAR has an independent Judiciary. It is responsible for the administration of justice and interprets the laws enacted by the legislature.
The systems practiced in Macao are prescribed by the Basic Law, the constitutional document of the MSAR which came into effect upon its establishment on December 20, 1999.
A.4 Historical Outline of Cadastral System
The land registration system has more than 100 years of history while cadastral system has only 20 years.
With the objective of providing a complete, reliable, computerized and constantly updated cadastral plan for Macao, the cadastral system was introduced in the 1980s. From 1983 to 1998, the Cartography and Cadastre Bureau conducted a full-scale systematic survey throughout the territory of Macao and in 1994 the Cadastral Act was passed. The Cadastral Act (Decreto-Lei nº3/94/M) and Land Registration Act (Decreto-Lei nº46/99/M) build the legal framework for cadastral surveying and land registration.
The Macao cadastre comprises more than ten thousand land parcels. The cadastral plans were published during 1994 to 1998 for the consultation of landowners and other users. They may order printouts of cadastral plans at a reasonable price.
B. Institutional Framework
B.1 Government Organizations
The Land Registry under the Secretary for Administration and Justice is responsible for land registration and Cartography and Cadastre Bureau under the Secretary for Transport and Public Works is responsible for cadastral surveying.
B.2 Private Sector Involvement
Land registration and cadastral surveying are the government's exclusive responsibilities.
B.3 Professional Organization or Association
There is no professional organization or association for cadastral surveyors.
B.4 Licensing
At present, there is no licensing system for cadastral surveying professionals. But a university degree in surveying is the prerequisite for entering the professional field as a surveyor and a 2-year diploma degree in surveying for assistant surveyors.
B.5 Education
The Survey and Cadastre School affiliated to Cartography and Cadastre Bureau offers a 2-year diploma program in surveying. Over the years, more than 200 students have graduated from the school. Some of them have entered the field of surveying and others have found their places in various sectors of the society, dedicating their knowledge and expertise to the building and development of Macao's thriving economy. So far, there is no local institution offering bachelor degree in surveying. All professional surveyors obtained their degrees from overseas institutions.
C. Cadastral System
C.1 Purpose of Cadastral System
The cadastres are based on the proprietary land parcel which is the area defined by ownership. The cadastral system is the legal basis for all dealings in land, such as planning, assessment, etc.
C.2 Types of Cadastral System
The cadastral system practised in Macao covers the complete territory. Not all the settlements are formal or legal but there is adverse possession in Macao. A person may apply for adverse possession for 20 years or above in accordance with the Land Law (Lei nº6/80/M).
C.3 Cadastral Concept
The land parcels are surveyed in the field by Cartography and Cadastre Bureau. Because the registration of land ownership is optional, Macao Cartography and Cadastre Bureau also takes the responsibility of collecting legal rights information such as land ownership, land grant document, lease term, etc.
C.4 Content of Cadastral System
Macao Cadastral systems comprises the following components:
- Textual Component – information retrieved from Cartography and Cadastre Bureau, Land Registry, Lands, Public Works and Transport Bureau, Civic and Municipal Affairs Bureau, Finance Bureau, etc.
- Spatial Component - Cadastral maps show all land parcels graphically corresponding to the owner or registered title with unique identifiers.
The cadastre covers more than ten thousand land parcels including private owned, grant and government land. Both cadastral records and land registers have been computerized. Cartography and Cadastre Bureau and Land Registry conclude an agreement on data exchange via the intranet.
D. Cadastral Mapping
D.1 Cadastral Map
The A4-size cadastral map contains textual and spatial information. The scale is determined depending on the size of parcel, from 1:500 to 1:8000. The map shows the parcel identifiers, registration number, tax identification number, location, boundary extent, dimensions, area, etc.
D.2 Example of a Cadastral Map
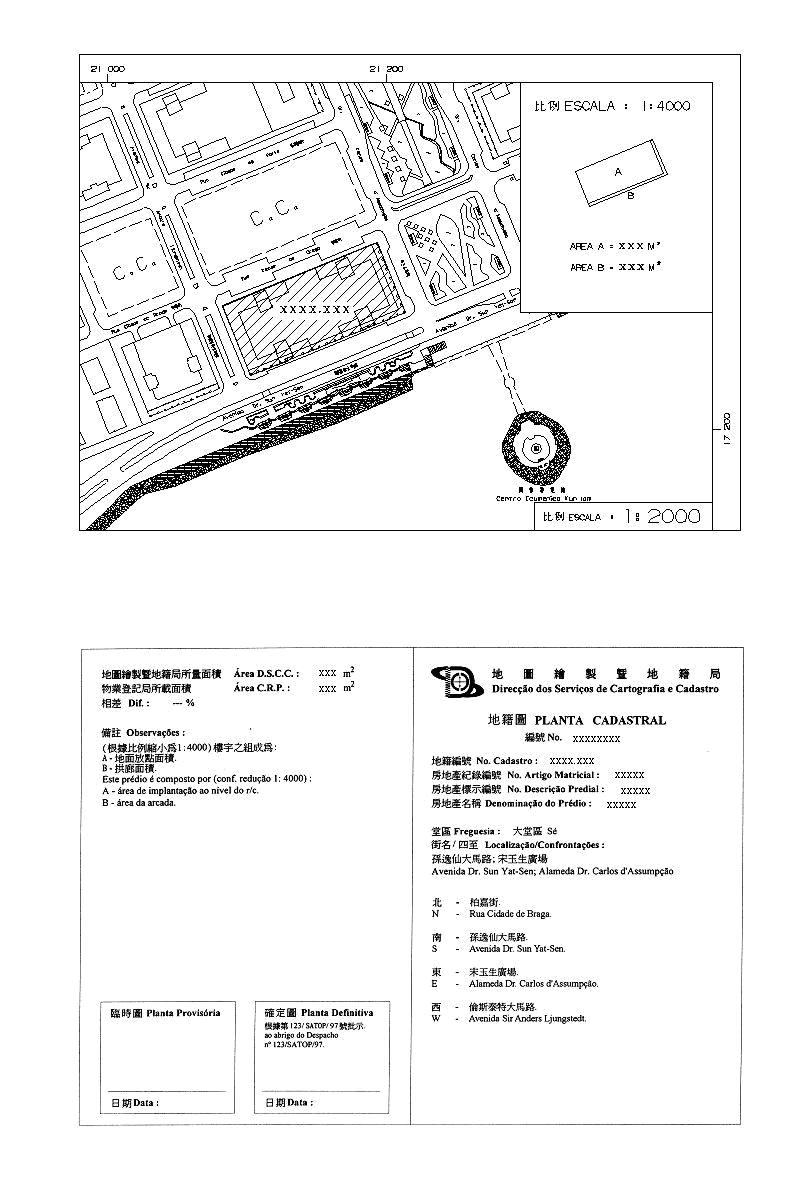
D.3 Role of Cadastral Layer in SDI
The cadastral map is widely used in many departments such as Lands, Public Works and Transport Bureau, Office of Infrastructure Development, Civic and Municipal Affairs Bureau, etc. There is no government department responsible for gathering different land information and managing them in one unique system.
E. Reform Issues
E.1 Cadastral Issues
- The land registration is optional.
- Land registration and cadastral surveying are operated by two different departments.
- As mentioned above, there is no government department responsible for gathering different land information and managing them in one unique system.
E.2 Current Initiatives
- The Land Registry encourages people to get their land registered by stressing the advantages prescribed by the Land Registration Act.
- The Cartography and Cadastre Bureau and Land Registry conclude an agreement on data exchange via the intranet.
- A new Cadastral Information System under construction will facilitate data integration. At present, we are trying to foster greater interdepartmental cooperation and collaboration as to provide better services and products.
F. References
http://www.macau.gov.mo/index_en.html
http://www.gis.gov.mo/dscc/engl/newfirst.htm
Part 2: Cadastral Principles and Statistics
1. Cadastral Principles
1.1 Type of registration system |
|
title registration
deeds registration |
1.2 Legal requirement for registration of land ownership |
|
compulsory
optional |
1.4 Approach for establishment of cadastral records |
|
systematic
sporadic both, systematic and sporadic all properties already registered |
2. Cadastral Statistics
2.1 Population |
441,600 |
2.2a Population distribution: percentage of population living in urban areas |
100 |
2.2b Population distribution: percentage of population living in rural areas |
0 |
2.3 Number of land parcels |
10,214 |
--- Number of land parcels per 1 million population |
23,100 |
2.4 Number of registered strata titles/condominium units |
0 |
--- Number of strata titles/condominium units per 1 million population |
0 |
2.5 Legal status of land parcels in URBAN areas: |
|
percentage of parcels that are properly registered and surveyed |
92 |
percentage of parcels that are legally occupied, but not registered or surveyed |
1 |
percentage of parcels that are informally occupied without legal title |
7 |
2.6 Legal status of land parcels in RURAL areas: |
|
percentage of parcels that are properly registered and surveyed |
0 |
percentage of parcels that are legally occupied, but not registered or surveyed |
0 |
percentage of parcels that are informally occupied without legal title |
0 |
2.7 Number of active professional land surveyors |
0 |
2.8 Proportion of time that active professional land surveyors commit for cadastral matters (%) |
0 |
--- Approx. full-time equivalent of land surveyors committed to cadastral matters |
0 |
2.9 Number of active lawyers/solicitors |
0 |
2.10 Proportion of time that active lawyers/solicitors commit for cadastral matters (%) |
0 |
--- Approx. full-time equivalent of active lawyers/solicitors committed to cadastral matters |
0 |